Badgirs
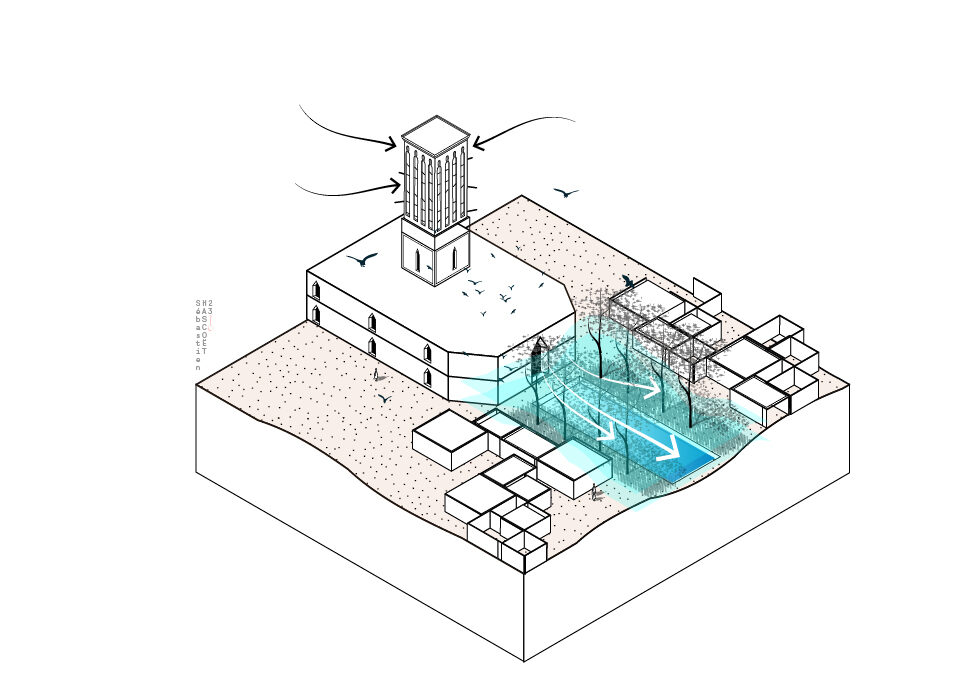
A 3,300-year-old Passive Geothermal System
A badgir is a natural ventilation system that uses the principles of air convection to cool building interiors in hot, dry places. When the warm outside air flows into the tower’s openings, it naturally descends through the chimney flue to the lower part of the building, which is also the coolest. The hot air, which is lighter, then rises up through the tower, creating suction. This effect then pushes a current of cool air down into the building interior.
The earliest badgirs or wind-catchers discovered date back about 3,300 years, in Egypt and Iran. The technology was subsequently honed in the Persian Empire, supplemented by a water basin placed at the base of the tower to further lower the air temperature. The city of Yazd was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2017 for its wind-catcher towers.
This passive geothermal system, which consumes zero energy, is a variation on the Canadian or Provençal well. It harnesses Earth’s natural temperature to cool the air.
Axonometry
Sebastien Hascoët
