The Unité d’Habitation, Le Corbusier
A Building with Connectivity and Sharing at its Core
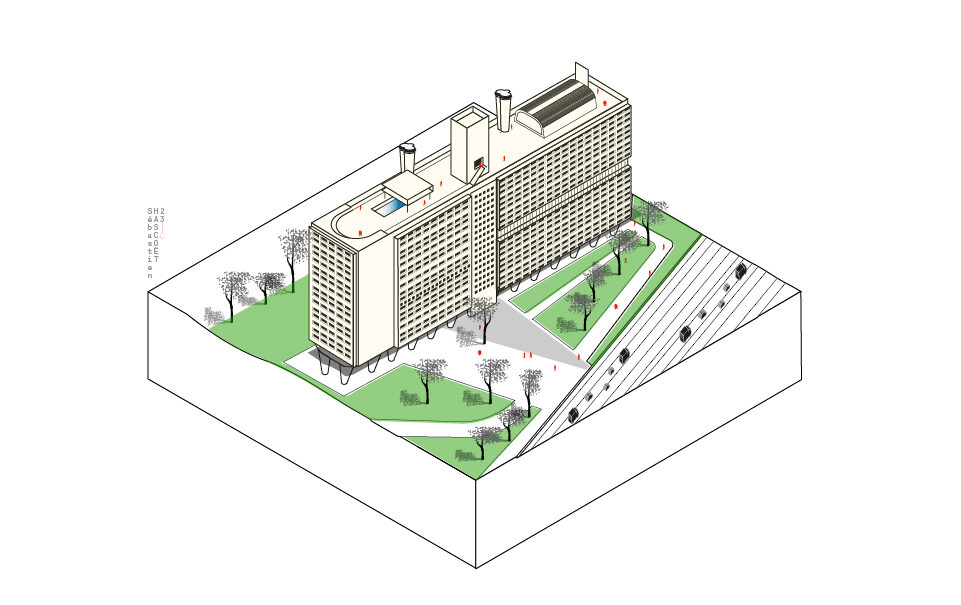
The Unité d’Habitation is the name given to a modern typology of residential buildings designed by Le Corbusier. Governed by the principle of the Modulor, a system of measurements linked to human morphology based on the golden ratio and Fibonacci numbers, the Unité d’Habitation was meant to be a “home for people”, a residential building promoting community life. All the services residents need to cultivate body and mind are included.
The Cité Radieuse in Marseille includes 337 apartments for about 1,600 residents as well as shops, sports facilities, a nursery school, and other amenities. A fine example of the common good driving a project. Spaces and services are thus shared, creating connection and togetherness between people which can then spark collective action.
Also, thanks to the stilts that raise the building off the ground, the footprint is reduced, allowing nature to claim its rightful place. The common good is thus turned outwards.
Axonometry
Sebastien Hascoët
